 Sources of ENERGY Sources of ENERGY
 |
We
use the word energy every day in different ways and meanings. Usually we have in
mind:
- electric,
- thermal,
- water,
- sun
- and nuclear energy
We don't even think where and how
this energy is saved. |
Power stations in Slovenia
The first power plant in Slovenia,
propelled by a steam engine, was built in 1883. Electric energy was produced by dynamo.
This power plant is on exhibition in Technical museum in Bistra.
Regarding supplied energy, we
distinguish four kinds of power plants:
- Hydroelectric power stations,
which
use water energy
- Steam power stations,
which use
chemical energy of fuels (coal, oil, gas.)
- Nuclear power stations,
which use
energy of fission of uranium nucleus.
- Power plants which use less common (alternative)
sources of energy (sun and wind energy, energy of ebb and flow, geothermic sources.)
Hydroelectric
power stations (HPP)
Soča power stations
Sava power stations
Drava power stations
The first bigger power station in
Slovenia was HPP Završnica in Gorenjska Region. It was built in 1915. There were also
first power lines and first local network.
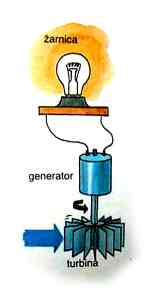
Water
contains energy because of its fall. Then it is transformed into mechanic and in the end
into electric energy.
With turbines we take energy
away from water (up to 85% of its energy).

Hydroelectric power station

the inside of HPP
Regarding
water conditions we use different kinds of turbines:
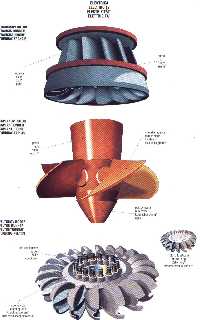
turbine
PELTON'S
TURBINE - uses bigger falls of water
KAPLAN'S TURBINE - uses larger amounts of water
FRANCIS'S TURBINE - in between
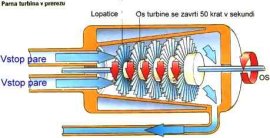
turbine_prerez
Steam
power stations (TPP)
- steam power station Šoštanj
- steam power station Brestovica
- steam power station Ljubljana
In steam power station chemical
energy is transformed into thermal energy, thermal energy into mechanical (steam turbines)
and mechanical into electric energy (generators). When fuel burns, water is getting warmed
and is transformed into steam.

premog
Steam propels steam turbine
with its energy and turbine propels generator over the shaft. Then the generator produces
electric energy. |
Nuclear power stations (NPP) nuclear station plant Krško

nuklearna Krško
At
nuclear fussion of atomic nucleus of uranium a lot of energy is
produced. This energy is used to heat water, which vaporizes. The steam moves spades of
steam turbine, which propels the generator.
This happens in the nuclear
reactor, which is some kind of an "oven" where the water is getting warmed.
Other types of
power stations

sun

wind
geoterm
Alternative sources
A minor part of energy is brought to us by
alternative sources: wind energy, tid e, sun cells, springs of hot water, etc.
s
un, tide
Solar energy:
We collect solar energy with solar cells.
There are three types of solar cells and these are called: AMORPHIC, CRISTAL and
POLICRISTAL solar cells.
Wind energy:
We collect this energy with special big wind
generators; the kinetic energy is exploited at this.
veter
Biomass:
Biomass is the dead parts of animals and
plants. We can extract biogas from biomasses, with the help of bacteria that decompose
biomasses into biogas and manure.
Hydrogen:
Industry processes are powered up with
hydrogen. Hydrogen is an ecological source because it burns into water, that's why it's
a perfect source of energy.
Most of the
energy comes from the sun. The sun heats us; this merit goes to the accumulated kinetic
energy in the fossil fuels (oil, natural gas and coal). Winds, flood tides and sea
currents also pump the energy from it. Example: Water that evaporates from the oceans, and
later falls down to the earth in the shape of rain, which powers the hydroelectric power
station.
The Sun receives its energy
from the pooling of hydrogen atom cores into helium cores.
Vapor
powers up the steam turbine and the turbine the generator by a shaft. The generator
produces electrical energy.
Energy that doesn't come from the sun:
- heat in the interior of the Earth
- nuclear fuel energy
- flood tide energy (consequence of the
gravitational attractiveness of theMoon)
Energy sources of the Earth
The main source of energy on the Earth is the solar radiation. The
consequences of this radiation are:
- maintaining of the temperature on Earth
- winds, sea currents and weather occurrences
- animal and plant life
- maintenance of the constant composition of
the atmosphere million years ago, made possible the existence of fossil fuels (oil,
natural gas, coil)
|

