
(a) \(\overrightarrow{CB}\)
(b) \(\overrightarrow{PC}\)
(c) \(\overrightarrow{AP}\)
Solutions: (a) \(\overrightarrow{CB}=\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}\); (b) \(\overrightarrow{PC}=-\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{a}+\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{b}\); (c) \(\overrightarrow{AP}=\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{a}+\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{b}\)(a) \(\overrightarrow{AC}\)
(b) \(\overrightarrow{ES}\)
(c) \(\overrightarrow{FC}\)
(d) \(\overrightarrow{EA}\)
Solutions: (a) \(\overrightarrow{AC}=\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\); (b) \(\overrightarrow{ES}=\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}\); (c) \(\overrightarrow{FC}=2\mathbf{a}\); (d) \(\overrightarrow{EA}=\mathbf{a}-2\mathbf{b}\)(a) \(\overrightarrow{AC}\)
(b) \(\overrightarrow{BD}\)
(c) \(\overrightarrow{AP}\)
(d) \(\overrightarrow{AU}\)
(e) \(\overrightarrow{PV}\)
Solutions: (a) \(\overrightarrow{AC}=\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\); (b) \(\overrightarrow{BD}=-\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\); (c) \(\overrightarrow{AP}=\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\); (d) \(\overrightarrow{AU}=\mathbf{a}+\frac{1}{3}\mathbf{b}\); (e) \(\overrightarrow{PV}=\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{a}-\frac{1}{3}\mathbf{b}\)(a) \(\overrightarrow{AB}\)
(b) \(\overrightarrow{DB}\)
(c) \(\overrightarrow{PD}\)
Solutions: (a) \(\overrightarrow{AB}=\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}\); (b) \(\overrightarrow{DB}=\mathbf{a}-2\mathbf{b}\); (c) \(\overrightarrow{PD}=-\mathbf{a}+\frac{3}{2}\mathbf{b}\)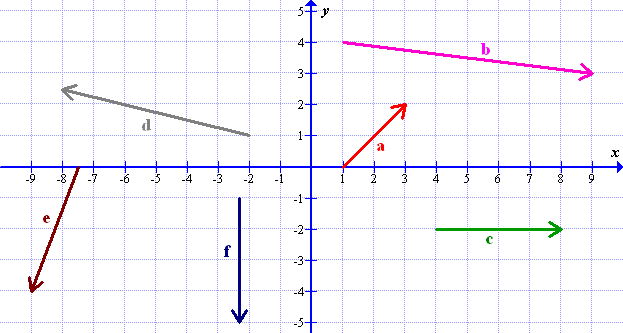
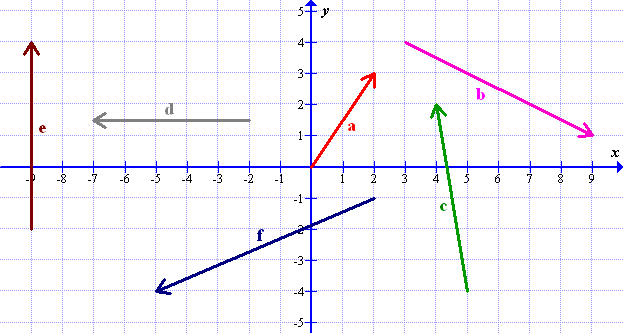
(a) Draw vectors \(\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\) and \(\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}\).
(b) Write vectors \(\mathbf{a}\) and \(\mathbf{b}\) in column notation.
(c) Calculate vectors \(\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\) and \(\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}\) and write them in column notation.
Solutions: (b) \(\mathbf{a}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 6 \\ 1 \end{array}\right)\), \(\mathbf{b}=\left(\begin{array}{c} -2 \\ 3 \end{array}\right)\); (c) \(\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 4 \\ 4 \end{array}\right)\), \(\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 8 \\ -2 \end{array}\right)\)(a) \(\mathbf{u}=\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\)
(b) \(\mathbf{v}=5\mathbf{a}-6\mathbf{b}\)
(c) \(\mathbf{w}=-\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{a}+\frac{2}{3}\mathbf{b}\)
Solutions: (a) \(\mathbf{u}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 16 \\ 15 \end{array}\right)\); (b) \(\mathbf{v}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 14 \\ -24 \end{array}\right)\); (c) \(\mathbf{w}=\left(\begin{array}{c} -1 \\ 3 \end{array}\right)\)(a) \(\mathbf{u}=\mathbf{a}+2\mathbf{b}\)
(b) \(\mathbf{v}=-\mathbf{a}+4\mathbf{b}\)
(c) \(\mathbf{w}=\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{b}\)
Solutions: (a) \(\mathbf{u}=14\mathbf{i}\); (b) \(\mathbf{v}=16\mathbf{i}+9\mathbf{j}\); (c) \(\mathbf{w}=-3\mathbf{i}-3\mathbf{j}\)(a) \(\frac{5}{2}\mathbf{a}\)
(b) \(2\mathbf{a}+3\mathbf{i}-\mathbf{j}\)
(c) \(|\mathbf{a}|\)
Solutions: (a) \(\frac{5}{2}\mathbf{a}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 20 \\ 15 \end{array}\right)\); (b) \(2\mathbf{a}+3\mathbf{i}-\mathbf{j}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 19 \\ 11 \end{array}\right)\); (c) \(|\mathbf{a}|=10\)(a) Find \(|\mathbf{a}|\) and \(|\mathbf{b}|\).
(b) Calculate \(\mathbf{c}=\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\).
(c) Find \(|\mathbf{c}|\).
Solutions: (a) \(|\mathbf{a}|=75,~~ |\mathbf{b}|=70\); (b) \(\mathbf{c}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 63 \\ 16 \end{array}\right)\); (c) \(|\mathbf{c}|=65\)(a) Find \(|\mathbf{a}|\).
(b) Write down the unit vector \(\mathbf{u}\) which has the direction of the vector \(\mathbf{a}\).
Solutions: (a) \(|\mathbf{a}|=10\); (b) \(\mathbf{u}=\left(\begin{array}{c} \frac{3}{5} \\ \frac{4}{5} \end{array}\right)\)(a) Show that \(\mathbf{u}_1\) and \(\mathbf{u}_2\) are unit vectors.
(b) Calculate \(|\mathbf{u}_1-\mathbf{u}_2|\) (write the exact value).
Solutions: (a) \(|\mathbf{u}_1|=1,~~ |\mathbf{u}_2|=1\); (b) \(|\mathbf{u}_1-\mathbf{u}_2|=\sqrt{3}\)(a) Write down the position vectors \(\overrightarrow{OA}\) and \(\overrightarrow{OB}\).
(b) Find the vector \(\overrightarrow{AB}\).
Solutions: (a) \(\overrightarrow{OA}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 3 \\ 1 \end{array}\right)\), \(\overrightarrow{OB}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 5 \\ 6 \end{array}\right)\); (b) \(\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{OB}-\overrightarrow{OA}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 2 \\ 5 \end{array}\right)\)(a) Find vectors \(\mathbf{u}=\overrightarrow{AB}\), \(\mathbf{v}=\overrightarrow{BC}\) and \(\mathbf{w}=\overrightarrow{CA}\).
(b) Verify that \(\mathbf{u}+\mathbf{v}+\mathbf{w}=\mathbf{0}\).
Solutions: (a) \(\mathbf{u}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 7 \\ 3 \end{array}\right)\), \(\mathbf{v}=\left(\begin{array}{c} -2 \\ 4 \end{array}\right)\), \(\mathbf{w}=\left(\begin{array}{c} -5 \\ -7 \end{array}\right)\); (b) \(\mathbf{u}+\mathbf{v}+\mathbf{w}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 0 \\ 0 \end{array}\right)\)(a) Find the coordinates of point \(D\).
(b) Find the length of the diagonal \(AC\)
Solutions: (a) \(D(3,7)\); (b) \(|\overrightarrow{AC}|=10\)(a) Find the coordinates of point \(C\).
(b) Find the coordinates of the intersection point of the diagonals \(AC\) and \(BD\).
Solutions: (a) \(C(7,9)\); (b) \(P(2,5)\)(a) Find the coordinates of points \(C\) and \(D\).
(b) Find the coordinates of point \(P\).
Solutions: (a) \(C(18,10),~ D(8,6)\); (b) \(P(12,5.5)\)(a) Show that \(ABCD\) is a parallelogram.
(b) Find the coordinates of the point \(P\) which is the intersection point of the diagonals.
(c) Find the length of the longer diagonal.
Solutions: (a) \(\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{DC}=\left(\begin{array}{c} 27 \\ -3 \end{array}\right)\) and \(\overrightarrow{AD}=\overrightarrow{BC}=\left(\begin{array}{c} -3 \\ 13 \end{array}\right)\); (b) \(P(7,5)\); (c) \(|\overrightarrow{BD}|=34\)(a) Find the coordinates of the point \(U\) on \(AB\) such that \(AU:UB=1:3\).
(b) Find the coordinates of the point \(V\) on \(AB\) such that \(AV:AB=1:3\).
Solutions: (a) \(U(14,14)\); (b) \(V(17,12)\)(a) Find the coordinates of the point \(A\).
(b) Find the coordinates the points \(P\) and \(R\).
(c) Write down the coordinates the vector \(\overrightarrow{PR}\).
(d) Show that the vector \(\overrightarrow{PR}\) is parallel to the vector \(\overrightarrow{BD}\).
Solutions: (a) \(A(5,1)\); (b) \(P(8,2),~ R(7,5)\); (c) \(\overrightarrow{PR}=\left(\begin{array}{c} -1 \\ 3 \end{array}\right)\); (d) \(\overrightarrow{BD}=4\cdot\overrightarrow{PR}\)(a) Express vector \(\mathbf{u}\) in terms of \(\mathbf{v}\) and \(\mathbf{w}\) if possible.
(b) Express vector \(\mathbf{w}\) in terms of \(\mathbf{u}\) and \(\mathbf{v}\) if possible.
Solutions: (a) \(\mathbf{u}=\frac{3}{2}\mathbf{v}+0\mathbf{w}\); (b) It's not possible.