
(a) Find the lengths of the other two sides \(b=AC\) and \(c=AB\).
(b) Calculate the perimeter \(P\) of the triangle.
Solutions: (a) \(b\approx10.5~\mathrm{cm},~ c\approx17.5~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(P=a+b+c\approx42.1~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) Find the lengths of the other two sides \(b=AC\) and \(c=AB\).
(b) Calculate the perimeter \(P\) of the triangle.
Solutions: (a) \(b=4\sqrt{3}~\mathrm{cm}\approx6.93~\mathrm{cm}\), \(c=8\sqrt{3}~\mathrm{cm}\approx13.9~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(P=a+b+c=12+12\sqrt{3}~\mathrm{cm}\approx32.8~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) Find the lengths of the other two sides.
(b) Calculate the perimeter \(P\) of the triangle.
Solutions: (a) \(a\approx13.5~\mathrm{cm},~ b\approx10.3~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(P=a+b+c\approx40.8~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) Find the length of the hypotenuse.
(b) Calculate the angles \(\alpha=B\hat{A}C\) and \(\beta=A\hat{B}C\).
Solutions: (a) \(c=AB=17~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(\alpha\approx61.9^\circ,~ \beta\approx28.1^\circ\)(a) Find the perimeter of this triangle.
(b) Calculate the angles \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\).
Solutions: (a) \(a=24~\mathrm{cm},~ P=56~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(\alpha\approx73.7^\circ,~ \beta\approx16.3^\circ\)(a) Find the length of the side \(c\).
(b) Find the length of the height \(h_c\).
Solutions: (a) \(c\approx5.24~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(h_c\approx6.49~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) Find the perimeter of this triangle.
(b) Calculate the angles of this triangle.
Solutions: (a) \(P=24+37+37=98~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(\alpha=\beta\approx71.1^\circ,~ \gamma\approx37.8^\circ\)(a) Find the sides of this rectangle.
(b) Calculate the acute angle between the diagonals.
Solutions: (a) \(a\approx17.7~\mathrm{cm},~ b\approx9.31~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(\varphi=55.5^\circ=55^\circ30'\)(a) Find the side \(a=AB\).
(b) Calculate the angle \(\alpha=D\hat{A}B\).
Solutions: (a) \(a=17~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(\alpha\approx56.1^\circ\)(a) Find the height to which the top of the ladder will reach.
(b) Calculate the angle between the wall and the ladder.
Solutions: (a) \(a\approx2.90~\mathrm{m}=290~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(\alpha\approx14.5^\circ\)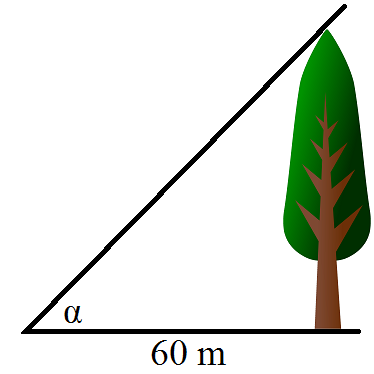 We are looking at a tree from the distance of 60 m. From a point on the ground the angle of elevation
of the top of this tree is 25°. Find the height of this tree.
We are looking at a tree from the distance of 60 m. From a point on the ground the angle of elevation
of the top of this tree is 25°. Find the height of this tree.
(a) Find the height \(h_c\).
(b) Find the distances \(AH\) and \(HB\).
(c) Hence, calculate the side \(a=BC\).
Solutions: (a) \(h_c\approx5.64~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(AH\approx2.05~\mathrm{cm},~ HB\approx7.95~\mathrm{cm}\); (c) \(a\approx9.74~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) Find the side \(b\).
(b) Calculate the angles \(\alpha\) and \(\gamma\).
Solutions: (a) \(b\approx32.4~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(\alpha\approx42.8^\circ,~ \gamma\approx30.2^\circ\)(a) Find the height \(h_c\).
(b) Calculate the side \(a\).
Solutions: (a) \(h_c=8~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(a\approx8.46~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) Find the angle \(\gamma\).
(b) Find the sides \(a\) and \(b\).
Solutions: (a) \(\gamma=52^\circ\); (b) \(a\approx16.0~\mathrm{cm},~ b\approx18.0~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) Find the angles \(\alpha\) and \(\gamma\).
(b) Find the side \(c\).
Solutions: (a) \(\alpha\approx35.8^\circ,~ \gamma\approx61.2^\circ\); (b) \(c\approx34.4~\mathrm{cm}\)
(a) Find the height \(h_c\).
(b) Find the area \(A\).
Solutions: (a) \(h_c=3~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(A=12~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the side \(b\).
(b) Find the area \(A\).
Solutions: (a) \(b\approx15.8~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(A\approx75.2~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the angle \(\alpha=C\hat{A}B\).
(b) Find the area \(A\).
Solutions: (a) \(\alpha=60^\circ\); (b) \(A=10\sqrt{3}~\mathrm{cm}\approx17.3~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the area.
(b) Find the height \(h_c\).
Solutions: (a) \(A=84~\mathrm{cm}^2\); (b) \(h_c=8~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) Find the angle \(\gamma\).
(b) Find the sides \(a\) and \(b\).
(c) Find the perimeter and area.
Solutions: (a) \(\gamma=73^\circ\); (b) \(a\approx9.21~\mathrm{cm},~ b\approx13.6~\mathrm{cm}\); (c) \(P\approx36.8~\mathrm{cm},~ A\approx59.8~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the diagonal \(f=BD\).
(b) Find the area of this parallelogram.
Solutions: (a) \(f=13~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(A\approx90.9~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the diagonal \(f=BD\).
(b) Find the height \(h\).
(c) Find the area of this rhombus.
Solutions: (a) \(f\approx7.93~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(h\approx6.54~\mathrm{cm}\); (c) \(A\approx45.7~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the side of this pentagon.
(b) Find the diagonal.
(c) Find the area.
Solutions: (a) \(a\approx9.40~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(d\approx15.2~\mathrm{cm}\); (c) \(A\approx152~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the diagonal \(AC\).
(b) Find the inradius \(r\) (radius of the inscribed circle).
(c) Find the area of this octagon.
Solutions: (a) \(AC\approx18.5~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(r\approx12.1~\mathrm{cm}\); (c) \(A\approx483~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the circumradius \(R\) (radius of the circumscribed circle).
(b) Find the length of the longest diagonal.
(c) Find the area of this nonagon.
Solutions: (a) \(R\approx8.77~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(d\approx17.3~\mathrm{cm}\); (c) \(A\approx223~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the area of this hexagon.
(b) Find the circumradius \(R\) (radius of the circumscribed circle).
(c) Find the inradius \(r\) (radius of the inscribed circle).
(d) By what percentage is the circumradius greater than the inradius?
Solutions: (a) \(A\approx665~\mathrm{cm}^2\); (b) \(R=a=16~\mathrm{cm}\); (c) \(r\approx13.9~\mathrm{cm}\); (d) By \(15.5\%\)(a) Find the circumference.
(b) Find the length of the arc with the central angle \(90^\circ\).
(c) Find the area of this circle.
(d) Find the area of the circular sector with the central angle \(90^\circ\).
Solutions: (a) \(P\approx62.8~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(L\approx15.7~\mathrm{cm}\); (c) \(A_0\approx314~\mathrm{cm}^2\); (d) \(A_1\approx78.5~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the length of the arc \(L\).
(b) Find the area of the corresponding circular sector.
Solutions: (a) \(L\approx18.1~\mathrm{cm}\); (b) \(A\approx135~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) Find the corresponding central angle.
(b) Find the length of the corresponding circular arc.
Solutions: (a) \(\theta\approx102^\circ\); (b) \(L=32~\mathrm{cm}\)(a) find the area of the circular sector,
(b) find the area of the corresponding circular segment.
Solutions: (a) \(A_1\approx50.3~\mathrm{cm}^2\); (b) \(A_2\approx18.3~\mathrm{cm}^2\)(a) \(30^\circ\)
(b) \(45^\circ\)
(c) \(120^\circ\)
(d) \(135^\circ\)
Solutions: (a) \(30^\circ=\frac{\pi}{6}\); (b) \(45^\circ=\frac{\pi}{4}\); (c) \(120^\circ=\frac{2\pi}{3}\); (d) \(135^\circ=\frac{3\pi}{4}\)(a) \(75^\circ\)
(b) \(20^\circ\)
(c) \(10^\circ\)
(d) \(1^\circ\)
Solutions: (a) \(75^\circ=\frac{5\pi}{12}\approx1.31\); (b) \(20^\circ=\frac{\pi}{9}\approx0.349\); (c) \(10^\circ=\frac{\pi}{18}\approx0.175\); (d) \(1^\circ=\frac{\pi}{180}\approx0.0175\)(a) \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
(b) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{5\pi}{6}\)
(d) \(\frac{5\pi}{4}\)
Solutions: (a) \(\frac{\pi}{3}=60^\circ\); (b) \(\frac{\pi}{2}=90^\circ\); (c) \(\frac{5\pi}{6}=150^\circ\); (d) \(\frac{5\pi}{4}=225^\circ\)(a) \(1\)
(b) \(0.25\)
(c) \(1.85\)
(d) \(3.14\)
Solutions: (a) \(1~\mathrm{rad}\approx57.3^\circ\); (b) \(0.25~\mathrm{rad}\approx14.3^\circ\); (c) \(1.85~\mathrm{rad}\approx106^\circ\); (d) \(3.14~\mathrm{rad}\approx180^\circ\)(a) find the area of the circular sector,
(b) find the length of the arc.
Solutions: (a) \(A\approx7.07~\mathrm{cm}^2\); (b) \(L\approx2.36~\mathrm{cm}\)