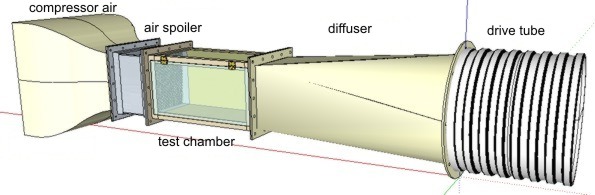
Parts of the wind tunnel - description
The wind tunnel consists of several components. These represent a specific
task assignment. Each part is independent and can be updated to upgrade or
completely replaced (needs change or malfunction). Parts are secured and sealing.
Featured are just the main parts of wind tunnel.

Compressor -
funnel:
The input
of the tunnel
where the device
absorbs the air
also serves
to compress the air mass.
Because of this latter
function, this is called the
compressor unit.
Air spoiler:
To avoid turbulent compressed air flowing into the test chamber which swirls air
and disrupts the relevant measurements, the router - spoiler allows horizontal
air streamlines. This is the only thing that is a prerequisite for comparative
measurement and determination of the air drag for bodies of different models.
Test chamber:
This is the main space of the wind tunnel, which is engaged with physical
measurement. Transparent doors and ceiling of the chamber allow for observing,
recording and noting the results of experiments. The rear wall is dimmed and
fitted with thin lines that allow detection of orientation of the fluids (fog or
smoke). The lower part of the chamber is equipped with the fixtures of the model
and the gear reduction mechanism for the force detectors and pressure.
Diffuser -
transition part of device:
The air flow between the chamber and the drive is enabled by reducing the
transition from a square cross-section to circle. In addition, section changes
also stretche air mass. The vacuum allows greater air flow and air velocity
through the test - measuring chamber.
Drive tube:
The drive system is installed in the pipe. Ventilator with DC motor drives the
air through the tunnel system elements. At the outlet - outlet is protected by a
metal mesh. This technological solution is not desirable, but necessary for
safety reasons.